Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shiba, Tomooki; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Ishimi, Akihiro
57th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM 2016), Vol.1, p.365 - 374, 2017/02
Fission products (FPs) such as Ce and Eu seem to be very low volatile even in high temperature environment in the severe accident of nuclear reactors. They are supposed to chemically coexist with nuclear fuel. In our passive gamma ray spectroscopy, gamma rays from such FPs are measured and their amount and burnup are estimated. Then we multiply the mass ratio of the FPs and nuclear materials, and we obtain the mass of nuclear material of interest. According to hypothetical fuel debris and canister models, we performed simulation of leakage gamma rays from canister of debris. gamma ray source spectra were derived from the composition of the hypothetical fuel debris and the photon transport calculation was carried out. In addition, we conducted experiments of gamma ray measurement from intact spent fuels irradiated in the Experimental Fast Reactor Joyo in order to validate the prediction performance of the simulation by the comparison of the experiments and simulation.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shirato, Atsuhiko*; Sato, Takashi*; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
From a viewpoint of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, it has recently become important to develop a non-destructive assay (NDA) system that accurately determines the amount of special nuclear materials (SNMs) in various samples such as spent fuels, next generation MA-Pu fuels and fuel debris. One candidate of those NDA techniques is neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). It relies on a neutron time-of-flight measurement and is a well-established method to apply for the accurate evaluations of nuclear data, including total cross sections and resonance parameters. The potential of NRTA to quantify SNM in complex materials has been already demonstrated by performing NRTA measurement at IRMM/GELINA under collaboration of JAEA and JRC. However, a present NRTA system usually has a large electron accelerator facility to generate intense neutrons, whereas this is very difficult to apply to various facilities that need to measure SNM. Therefore a compact NRTA system would be required for practical applications of quantifying SNM in a variety of samples. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we are developing a prototype with a D-T neutron generator that has a pulse width of 10  s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from
s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from 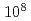 n/s to
n/s to 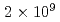 n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Tobita, Hiroshi; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J. M.*; Varasano, G.*; Pedersen, B.*
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The JAEA and EC/JRC have started collaborative research to develop a technique that can be utilized for quantification of high radioactive special nuclear materials such as next generation minor actinide fuels. In the study of a Differential Die-Away (DDA) technique, which is one of the techniques to be improved in the collaborative research, JRC type and JAEA type DDA techniques are compared. In the JRC type DDA technique, large amount of thermal neutron is generated using D-T neutron generator and graphite moderator to accomplish high detection sensitivity for small amount of fissile material. On the other hand, in JAEA type, relatively hard neutron spectrum and moderation of neutron in the target matrix are utilized to minimize position dependence of detection efficiency. Estimation of the neutron field is important to evaluate the performance of the system in DDA technique. The purpose of this study is to validate simulation results by experimental results and evaluate neutron flux distribution in the system by the simulation and the experiment. In this paper, we present the evaluation results of the neutron flux distributions in PUNITA which utilizes JRC type DDA technique and JAWAS-T which utilizes JAEA type DDA technique obtained by Monte Carlo simulation and activation method.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Maeda, Makoto; Ozu, Akira; Tobita, Hiroshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
Under the collaboration program with EC Joint Research Center, we have carried out the R&D program "Development of active neutron NDA techniques for nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security" with DDA (Differential Die-away Analysis), NRTA, PGA / NRCA and DGS. In this paper, we presents the outline of the current activity and study on next generation DDA. The goal of this study is to establish the DDA technique for high radiation nuclear materials with small measurement uncertainty. Lastly simulation study on newly developed prototype system "Active-N" which will be constructed at JAEA/NUCEF/BECKY facility in 2017 is presented.
Nomi, Takayoshi; Kawakubo, Yoko; Nagatani, Taketeru; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi; Menlove, H. O.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Browne, M. C.*
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Tobita, Hiroshi; Hattori, Kentaro; Shimofusa, Taichi; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
We are working on the development of a non-destructive assay (NDA) measurement system using the Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) method. The FNDI method is a kind of active neutron technique and can measure the total amounts of fissile materials (U-235, Pu-239, Pu-241). We have already carried out design analyses of an NDA measurement system for measuring the debris assuming use of the Three Mile Island (TMI) canister model. The result was presented at the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM) 56th Annual Meeting. Since then, we have modified the design of the NDA measurement system for the fuel debris and canister models at 1F. In this paper, we provide the calculation and evaluation results using the modified NDA measurement system. Moreover, we provide analytical investigations of the influence of fuel debris including high fissile material content on measurements.
Okazaki, Hiro; Shibano, Koya; Abe, Katsuo; Sumi, Mika; Kayano, Masashi; Kageyama, Tomio; Mason, P.*
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2016/07
The reference materials used for accountancy analysis by IDMS, referred to as LSD spikes allows to obtain accurate measurement results for a variety of nuclear materials under potentially difficult handling or measurement conditions. Because of expected difficulties in a stably long term supply of plutonium reference materials, which are the main source of plutonium for LSD spikes preparation, the JAEA's PFDC decided to evaluate the possibility of using domestically available MOX powders as a plutonium source material for LSD spikes. Therefore, PFDC started to separate, purify and characterize plutonium in MOX powders for plutonium reference materials (MOX-Pu) preparation that are suitable for source of LSD spikes in cooperation with the US DOE's NBL. The detailed preparation procedure of the latest MOX-Pu standard material and results of intercomparison for verification are presented.
Matsuki, Takuya; Masui, Kenji; Sekine, Megumi; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Yasuda, Takeshi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Ishiyama, Koichi; Nishida, Naoki; Horigome, Kazushi; Mukai, Yasunobu; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its long-term research and development (R&D) plan, development of a real-time measurement technology to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously as part of an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities. Since the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) has solutions containing both Pu and fission products (FP), a new detector development project to monitor Pu with FP is being carried out from 2015 to 2017. This project is mainly conducted in the High Active Liquid Waste Storage (HALWS) in the TRP. For the first step of this project, as the confirmation of composition of high active liquid waste (HALW) to evaluate neutron/ -ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted
-ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted  -ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/
-ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/ -ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/
-ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/ -ray detector. In this paper, we report three
-ray detector. In this paper, we report three  -ray peaks related with
-ray peaks related with  Pu and
Pu and  Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Holland, M. K.*; Cordaro, J. V.*; Morales-Arteaga, M. E.*; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Since 2007, the laboratory at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) have collaborated on a new mission to apply controlled-potential coulometry as a primary method for characterizating plutonium master solutions. Measurement results are being used to prepare traceable and certifiable large-size dry (LSD) spike standards for safeguards measurements by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The collaboration activities performed by JAEA and SRNL were authorized and funded under the JAEA & United States NNSA/DOE Permanent Coordinating Group. This report will chronicle the collaboration activities of JAEA and SRNL, and provide the detail on the periodic coulometer component calibration, the coulometric plutonium measures and measure practices, including the uncertainty propagation for the most recent plutonium master solution used for LSD Spike preparation.
Nakamura, Hironobu; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Makino, Risa; Mukai, Yasunobu; Ishiyama, Koichi; Kurita, Tsutomu; Ikeda, Atsushi*; Yamaguchi, Katsuhiro*
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
Regarding the Integrated Safeguards (IS) in Japan, the implementation of IS has been started on September 2004, and the concept has been introduced to the JNC-1 facilities since August 2008. Then, random interim inspection with short notice and reducing person-days of inspection (PDI) was introduced instead of traditional scheduled IIV in order to improve deterrence of the nuclear material diversion with timeliness goal. And it was agreed that it should be evaluated and reviewed because RII was designed when inter-campaign. In JAEA, we decided to restart PCDF campaign to reduce potential safety risks of reprocessing facilities. To adopt the RII scheme to the process operation in campaign, JAEA proposed a new scheme to JSGO and IAEA without increasing PDI and reducing detection probability. As a result of the discussion, it was agreed and successfully introduced since March 2014. The new scheme for PCDF consists of scheduled inspection (fixed-day RII), reduction of estimated material for the verification, implementation of remote monitoring with data provision, improvement of operational status check list, introduction of NRTA and MC&A data declaration with timeliness. Though the operator's workloads for information provision were increased, we could manage to balance IS requirement with implementation of our operation successfully. This contribution was helped to safeguards implementation and our operation for 2 years.
Sekine, Megumi; Matsuki, Takuya; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Mukai, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Yasuyuki; Nakamura, Hironobu; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its long-term research and development plan, development of a real-time measurement technology to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously as part of an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities. In the reprocessing plant, since solutions containing both Pu and FP exist, a new detector development project to monitor Pu with FP is being carried out from 2015 to 2017. This project is mainly conducted in the High Active Liquid Waste Storage (HALWS) in Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP). In this paper, an overview of the technology development, simulation results of preliminary evaluation of the characteristics of radiation emitted from the HALW tank at TRP, and the future research plan are presented.
Mukai, Yasunobu; Ogawa, Tsuyoshi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Kurita, Tsutomu; Sekine, Megumi; Rodriguez, D.; Takamine, Jun; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Seya, Michio
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2016/07
The development of Delayed Gamma-ray Spectroscopy (DGS) for analyzing the composition ratio of fissile nuclides ( Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  U) focused on the Delayed Gamma-ray having energy over 3 MeV has been performed for the development of active neutron non-destructive assay techniques. In PCDF, measurement tests of Delayed Gamma-ray using Pu solution and MOX powder samples to prove the DGS technique is planned to be performed in following 4 stages. (1) Measurements for Delayed Gamma-ray originated from spontaneous fission nuclide (Passive), (2) Measurements for the Delayed Gamma-ray with fast neutron (Active), (3) DGSI (DGS combined with self-interrogation) measurements (Passive), (4) Measurements for the Delayed Gamma-ray with thermal neutron (Active) In this paper, the plan of measurement tests for nuclear material samples with use of DGS is presented.
U) focused on the Delayed Gamma-ray having energy over 3 MeV has been performed for the development of active neutron non-destructive assay techniques. In PCDF, measurement tests of Delayed Gamma-ray using Pu solution and MOX powder samples to prove the DGS technique is planned to be performed in following 4 stages. (1) Measurements for Delayed Gamma-ray originated from spontaneous fission nuclide (Passive), (2) Measurements for the Delayed Gamma-ray with fast neutron (Active), (3) DGSI (DGS combined with self-interrogation) measurements (Passive), (4) Measurements for the Delayed Gamma-ray with thermal neutron (Active) In this paper, the plan of measurement tests for nuclear material samples with use of DGS is presented.
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Rossi, F.; Seya, Michio; Rodriguez, D.; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
Omer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Angell, C.*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Seya, Michio; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
Isotope-specific  -rays emitted in the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) process provide a good technique for a non-destructive detection and assay of nuclear materials. We are developing technologies relevant to
-rays emitted in the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) process provide a good technique for a non-destructive detection and assay of nuclear materials. We are developing technologies relevant to  -ray nondestructive detection and assay utilizing NRF. A Monte Carlo code to simulate NRF process is necessary for design and evaluation of NDA systems. We are developing NRFGeant4, a Geant4-based simulation code, for this purpose. In NRF experiments, highly-enriched targets are generally used such that the NRF signals are dominant and easily measured. In contrast, a real situation may involve very small contents of isotopes of interest. This results in a difficulty in measuring NRF signals because of the interference with other interactions, e.g. elastic scattering. For example, a typical nuclear fuel pellet contains about 90% of
-ray nondestructive detection and assay utilizing NRF. A Monte Carlo code to simulate NRF process is necessary for design and evaluation of NDA systems. We are developing NRFGeant4, a Geant4-based simulation code, for this purpose. In NRF experiments, highly-enriched targets are generally used such that the NRF signals are dominant and easily measured. In contrast, a real situation may involve very small contents of isotopes of interest. This results in a difficulty in measuring NRF signals because of the interference with other interactions, e.g. elastic scattering. For example, a typical nuclear fuel pellet contains about 90% of  U as a host material and less than 1% of
U as a host material and less than 1% of  Pu as an isotope of interest. When measuring NRF of
Pu as an isotope of interest. When measuring NRF of  Pu, there would be a huge background coming from the elastic scattering of
Pu, there would be a huge background coming from the elastic scattering of  U. Therefore, an estimation of the elastic scattering with the host material is essential for precise determination of isotope of interest. Satisfying estimation of elastic scattering is currently not available except for some calculations. In the present study, we upgrade our simulation code to include the calculation of elastic scattering events.
U. Therefore, an estimation of the elastic scattering with the host material is essential for precise determination of isotope of interest. Satisfying estimation of elastic scattering is currently not available except for some calculations. In the present study, we upgrade our simulation code to include the calculation of elastic scattering events.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Komeda, Masao; Shiba, Tomooki; Maeda, Makoto; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Mason, P.*; Sumi, Mika; Kageyama, Tomio; Suzuki, Toru; Holland, M. K.*; Cordaro, J.*
no journal, ,
In the early 2000's it had become clear that Japanese fuel cycle facilities would require plutonium RMs needed to perform a large number of accountancy measurements beyond the capacity of the producers. Additionally, the increasing difficulty in producing plutonium CRMs would further limit the amount of imported plutonium RMs available for safeguards. In order to help address the issue, in 2003 the US DOE's NNSA and JAEA began a cooperation to develop Japanese capabilities for plutonium RM production. Under this auspices, the DOE's NBL and JAEA's PFDC began efforts to establish plutonium RM production capability. In 2013 the DOE's SRNL established a similar cooperative agreement with JAEA's TRP to develop and maintain expertise in plutonium coulometry. This paper will discuss the development and status of these efforts and others.